API-Based Integrations
Integrations operated via API are used when the integration is handling smaller amounts of data, and the integration offering requires synchronous feedback about the result of transmitting an entity. These offerings should be designed to account for performance and socket impact on the integrated system(s) by using batch operations as well as retry and fallback/throttling mechanisms.
Endpoint URLs and API entity transformation rules are prime candidates for storage in the Configuration Service.
Asynchronous Integration Using Azure Service Bus
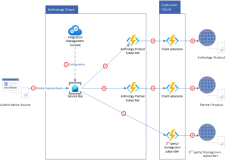
The asynchronous model is a "publish-subscribe" model wherein an Anthology source product publishes business events to the Azure Service Bus, and any system attached to the customer's cloud can subscribe to the events. This is a one-way message flow, i.e., the source system does not expect a response from the target systems.
Anthology's roadmap includes expanding its product integration capabilities using the Azure Service Bus.
Azure Service Bus is a fully managed enterprise message broker with message queues and publish-subscribe topics (in a namespace). Service Bus is used to decouple applications and services from each other, providing the following benefits:
-
Load-balancing work across competing workers
-
Safely routing and transferring data and control across service and application boundaries
-
Coordinating transactional work that requires a high degree of reliability
For more details refer to What is Azure Service Bus?
-
The Authoritative Source publishes a business event to the Service Bus.
-
The Service Bus uses configuration information to validate subscribers.
-
Anthology product or partner functions retrieve messages from the Service Bus and process business logic.
-
Anthology product functions pass messages to client extension functions for client-specific business logic.
-
Messages are published to the subscribing system.
Synchronous Integration Using APIs
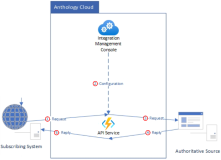
The synchronous model introduces an API Service that handles incoming and outgoing messages between the source and target systems. The API Service responds to requests from the subscribing systems. Based on the configuration, the API Service identifies the authoritative source and determines which subscribing system is to receive the reply.
Anthology APIs are published securely for internal and external developers.
-
The subscribing system sends API requests to the API Service.
-
The API Service uses configuration information to find the Authoritative Source.
-
The API Service sends API requests to the authoritative source.
-
Responses are passed back to the API Service.
-
The API Service receives responses and sends them to the subscribing system.
Authoritative Source
The Authoritative Source (also referred to as the "System of Truth") is defined for the following entities:
| Authoritative Source | Entities |
|---|---|
|
Anthology Student |
Students Transcripts Financial Aid Student BIlling Courses Grades Advising |
|
Finance & HCM |
General Ledger Fund Sources AP (Accounts Payable) / AR (Accounts Receivable) Staff / Workers Jobs Positions |
|
Anthology Reach |
People Organizations Communications Cases |
|
Blackboard Learn |
Attendance Lessons Lesson Grades Student Activity |